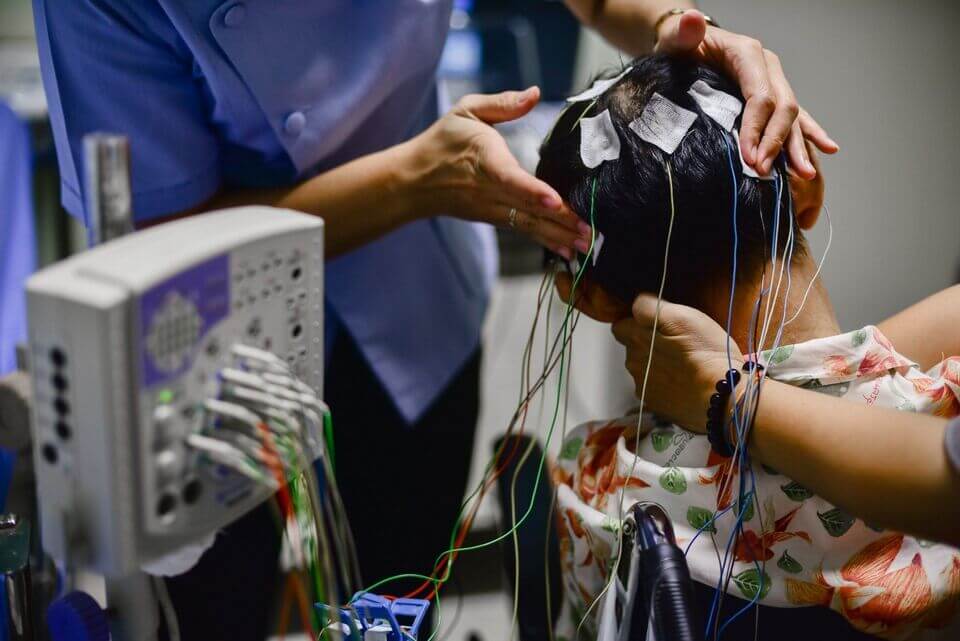
EEG
An EEG records the brain’s spontaneous electrical activity over a short period of time from multiple electrodes placed on the scalp. The electrodes sense tiny electrical charges created by the activity of your brain cells.
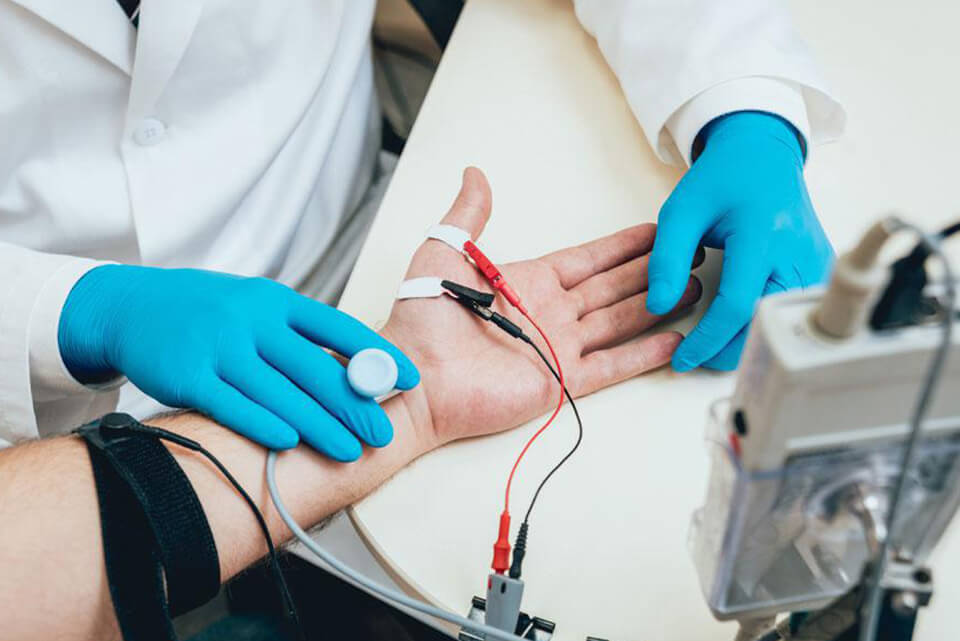
EMG
The electromyography procedure enables the diagnosis of peripheral nerve problems and muscle problems based on the information obtained from the physical examination. Electrical activity of muscles is recorded as a graph.
NCS
Nerve Conduction Studies are used to record how well and how quickly the nerves in the body send electrical impulses. The test is used to check various disorders of the peripheral nervous system.
VEP
The visual evoked potential or visual evoked response (VEP) measures the activity of the brain’s occipital area in response to visual stimuli.
BAER
(BAEP) measures electrical activity in the cochlea and auditory pathways in the brain. The response is collected with an extremely small electrical probe placed under the scalp: one between the shoulder blades, one in front of each ear, and one at the top of the head.
SSEP
The SSEP test measures the sensory pathway as an electrical signal travels from the nerve endings in the hands and/or legs to the brain. It is used to determine whether there is an interruption in the sensory pathway.